app开发者平台在数字化时代的重要性与发展趋势解析
809
2022-11-05

JVM堆外内存源码完全解读分析
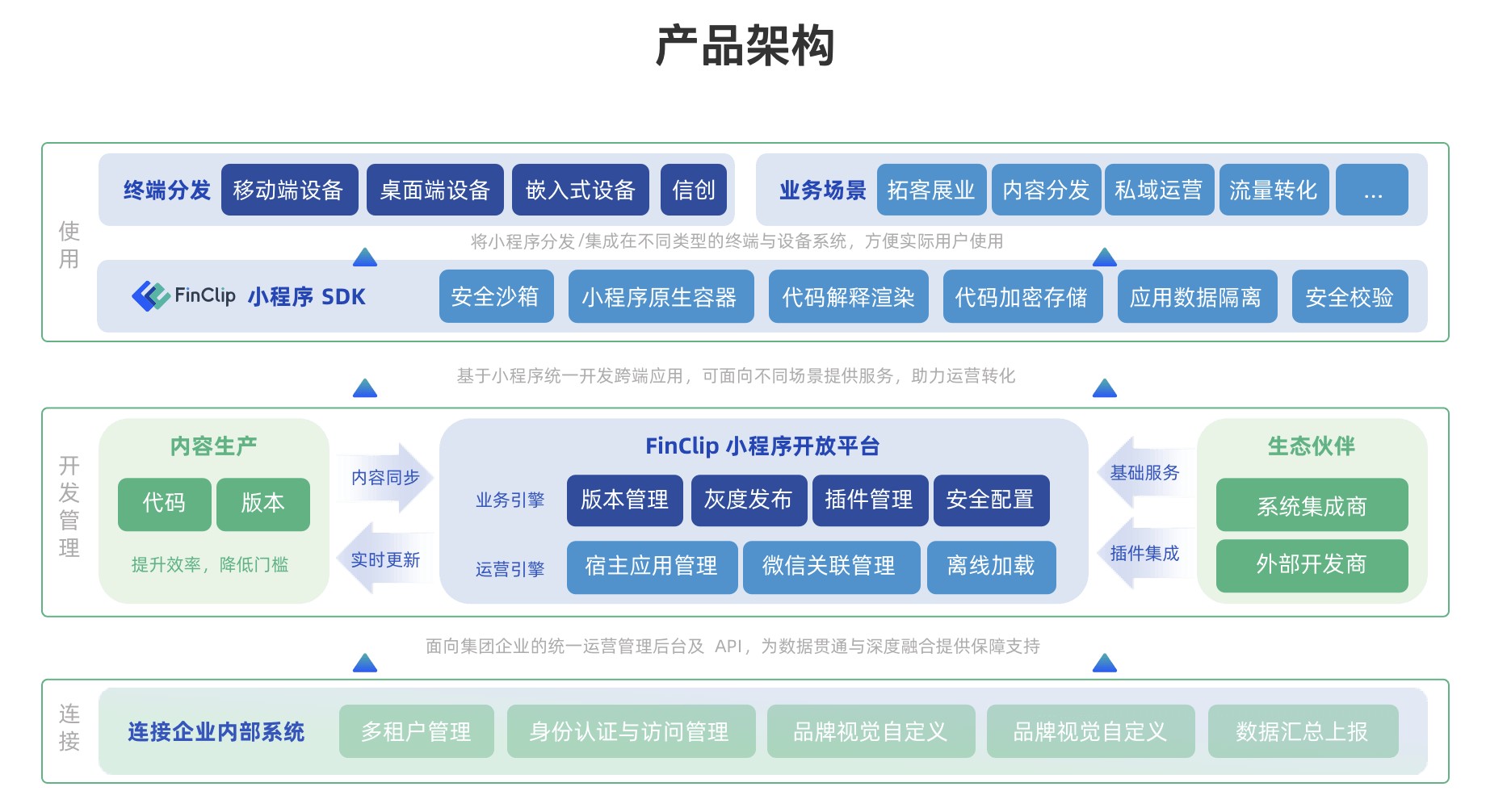
概述
广义的堆外内存
说到堆外内存,那大家肯定想到堆内内存,这也是我们大家接触最多的,我们在jvm参数里通常设置-Xmx来指定我们的堆的最大值,不过这还不是我们理解的java堆,-Xmx的值是新生代和老生代的和的最大值,我们在jvm参数里通常还会加一个参数-XX:MaxPermSize来指定持久代的最大值,那么我们认识的Java堆的最大值其实是-Xmx和-XX:MaxPermSize的总和,在分代算法下,新生代,老生代和持久代是连续的虚拟地址,因为它们是一起分配的,那么剩下的都可以认为是堆外内存(广义的)了,这些包括了jvm本身在运行过程中分配的内存,codecache,jni里分配的内存,DirectByteBuffer分配的内存等等
狭义的堆外内存
而作为java开发者,我们常说的堆外内存溢出了,其实是狭义的堆外内存,这个主要是指java.nio.DirectByteBuffer在创建的时候分配内存,我们这篇文章里也主要是讲狭义的堆外内存,因为它和我们平时碰到的问题比较密切
JDK/JVM里DirectByteBuffer的实现
DirectByteBuffer通常用在通信过程中做缓冲池,在mina,netty等nio框架中屡见不鲜,先来看看JDK里的实现:
DirectByteBuffer(int cap) { // package-private
super(-1, 0, cap, cap);
boolean pa = VM.isDirectMemoryPageAligned();
int ps = Bits.pageSize();
long size = Math.max(1L, (long)cap + (pa ? ps : 0));
Bits.reserveMemory(size, cap);
long base = 0;
try {
base = unsafe.allocateMemory(size);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError x) {
Bits.unreserveMemory(size, cap);
throw x;
}
unsafe.setMemory(base, size, (byte) 0);
if (pa && (base % ps != 0)) {
// Round up to page boundary
address = base + ps - (base & (ps - 1));
} else {
address = base;
}
cleaner = Cleaner.create(this, new Deallocator(base, size, cap));
att = null;
}
通过上面的构造函数我们知道,真正的内存分配是使用的Bits.reserveMemory方法
static void reserveMemory(long size, int cap) {
synchronized (Bits.class) {
if (!memoryLimitSet && VM.isBooted()) {
maxMemory = VM.maxDirectMemory();
memoryLimitSet = true;
}
// -XX:MaxDirectMemorySize limits the total capacity rather than the
// actual memory usage, which will differ when buffers are page
// aligned.
if (cap <= maxMemory - totalCapacity) {
reservedMemory += size;
totalCapacity += cap;
count++;
return;
}
}
System.gc();
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException x) {
// Restore interrupt status
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
synchronized (Bits.class) {
if (totalCapacity + cap > maxMemory)
throw new OutOfMemoryError("Direct buffer memory");
reservedMemory += size;
totalCapacity += cap;
count++;
}
}
通过上面的代码我们知道可以通过-XX:MaxDirectMemorySize来指定最大的堆外内存,那么我们首先引入两个问题
堆外内存默认是多大为什么要主动调用System.gc()
堆外内存默认是多大
如果我们没有通过-XX:MaxDirectMemorySize来指定最大的堆外内存,那么默认的最大堆外内存是多少呢,我们还是通过代码来分析
上面的代码里我们看到调用了sun.misc.VM.maxDirectMemory()
private static long directMemory = 64 * 1024 * 1024;
// Returns the maximum amount of allocatable direct buffer memory.
// The directMemory variablNctkrXFAde is initialized during system initialization
// in the saveAndRemoveProperties method.
//
public static long maxDirectMemory() {
return directMemory;
}
看到上面的代码之后是不是误以为默认的最大值是64M?其实不是的,说到这个值得从java.lang.System这个类的初始化说起
/**
* Initialize the system class. Called after thread initialization.
*/
private static void initializeSystemClass() {
// VM might invoke JNU_NewStringPlatform() to set those encoding
// sensitive properties (user.home, user.name, boot.class.path, etc.)
// during "props" initialization, in which it may need access, via
// System.getProperty(), to the related system encoding property that
// have been initialized (put into "props") at early stage of the
// initialization. So make sure the "props" is available at the
// very beginning of the initialization and all system properties to
// be put into it directly.
props = new Properties();
initProperties(props); // initialized by the VM
// There are certain system configurations that may be controlled by
// VM options such as the maximum amount of direct memory and
// Integer cache size used to support the object identity semantics
// of autoboxing. Typically, the library will obtain these values
// from the properties set by the VM. If the properties are for
// internal implementation use only, these properties should be
// removed from the system properties.
//
// See java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache and the
// sun.misc.VM.saveAndRemoveProperties method for example.
//
// Save a private copy of the system properties object that
// can only be accessed by the internal implementation. Remove
// certain system properties that are not intended for public access.
sun.misc.VM.saveAndRemoveProperties(props);
......
sun.misc.VM.booted();
}
上面这个方法在jvm启动的时候对System这个类做初始化的时候执行的,因此执行时间非常早,我们看到里面调用了sun.misc.VM.saveAndRemoveProperties(props)
public static void saveAndRemoveProperties(Properties props) {
if (booted)
throw new IllegalStateException("System initialization has completed");
savedProps.putAll(props);
// Set the maximum amount of direct memory. This value is controlled
// by the vm option -XX:MaxDirectMemorySize=
// The maximum amount of allocatable direct buffer memory (in bytes)
// from the system property sun.nio.MaxDirectMemorySize set by the VM.
// The system property will be removed.
String s = (String)props.remove("sun.nio.MaxDirectMemorySize");
if (s != null) {
if (s.equals("-1")) {
// -XX:MaxDirectMemorySize not given, take default
directMemory = Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory();
} else {
long l = Long.parseLong(s);
if (l > -1)
directMemory = l;
}
}
// Check if direct buffers should be page aligned
s = (String)props.remove("sun.nio.PageAlignDirectMemory");
if ("true".equals(s))
pageAlignDirectMemory = true;
// Set a boolean to determine whether ClassLoader.loadClass accepts
// array syntax. This value is controlled by the system property
// "sun.lang.ClassLoader.allowArraySyntax".
s = props.getProperty("sun.lang.ClassLoader.allowArraySyntax");
allowArraySyntax = (s == null
? defaultAllowArraySyntax
: Boolean.parseBoolean(s));
// Remove other private system properties
// used by java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache
props.remove("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
// used by java.util.zip.ZipFile
props.remove("sun.zip.disableMemoryMapping");
// used by sun.launcher.LauncherHelper
props.remove("sun.java.launcher.diag");
}
如果我们通过-Dsun.nio.MaxDirectMemorySize指定了这个属性,只要它不等于-1,那效果和加了-XX:MaxDirectMemorySize一样的,如果两个参数都没指定,那么最大堆外内存的值来自于directMemory = Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory(),这是一个native方法
JNIEXPORT jlong JNICALL
Java_java_lang_Runtime_maxMemory(JNIEnv *env, jobject this)
{
return JVM_MaxMemory();
}
JVM_ENTRY_NO_ENV(jlong, JVM_MaxMemory(void))
JVMWrapper("JVM_MaxMemory");
size_t n = Universe::heap()->max_capacity();
return convert_size_t_to_jlong(n);
JVM_END
其中在我们使用cms GC的情况下的实现如下,其实是新生代的最大值-一个survivor的大小+老生代的最大值,也就是我们设置的-Xmx的值里除去一个survivor的大小就是默认的堆外内存的大小了
size_t GenCollectedHeap::max_capacity() const {
size_t res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < _n_gens; i++) {
res += _gens[i]->max_capacity();
}
return res;
}
size_t DefNewGeneration::max_capacity() const {
const size_t alignment = GenCollectedHeap::heap()->collector_policy()->min_alignment();
const size_t reserved_bytes = reserved().byte_size();
return reserved_bytes - compute_survivor_size(reserved_bytes, alignment);
}
size_t Generation::max_capacity() const {
return reserved().byte_size();
}
为什么要主动调用System.gc
既然要调用System.gc,那肯定是想通过触发一次gc操作来回收堆外内存,不过我想先说的是堆外内存不会对gc造成什么影响(这里的System.gc除外),但是堆外内存的回收其实依赖于我们的gc机制,首先我们要知道在java层面和我们在堆外分配的这块内存关联的只有与之关联的DirectByteBuffer对象了,它记录了这块内存的基地址以及大小,那么既然和gc也有关,那就是gc能通过操作DirectByteBuffer对象来间接操作对应的堆外内存了。DirectByteBuffer对象在创建的时候关联了一个PhantomReference,说到PhantomReference它其实主要是用来跟踪对象何时被回收的,它不能影响gc决策,但是gc过程中如果发现某个对象除了只有PhantomReference引用它之外,并没有其他的地方引用它了,那将会把这个引用放到java.lang.ref.Reference.pending队列里,在gc完毕的时候通知ReferenceHandler这个守护线程去执行一些后置处理,而DirectByteBuffer关联的PhantomReference是PhantomReference的一个子类,在最终的处理里会通过Unsafe的free接口来释放DirectByteBuffer对应的堆外内存块
JDK里ReferenceHandler的实现:
private static class ReferenceHandler extends Thread {
ReferenceHandler(ThreadGroup g, String name) {
super(g, name);
}
public void run() {
for (;;) {
Reference r;
synchronized (lock) {
if (pending != null) {
r = pending;
Reference rn = r.next;
pending = (rn == r) ? null : rn;
r.next = r;
} else {
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException x) { }
continue;
}
}
// Fast path for cleaners
if (r instanceof Cleaner) {
((Cleaner)r).clean();
continue;
}
ReferenceQueue q = r.queue;
if (q != ReferenceQueue.NULL) q.enqueue(r);
}
}
}
可见如果pending为空的时候,会通过lock.wait()一直等在那里,其中唤醒的动作是在jvm里做的,当gc完成之后会调用如下的方法VM_GC_Operation::doit_epilogue(),在方法末尾会调用lock的notify操作,至于pending队列什么时候将引用放进去的,其实是在gc的引用处理逻辑中放进去的,针对引用的处理后面可以专门写篇文章来介绍
void VM_GC_Operation::doit_epilogue() {
assert(Thread::current()->is_Java_thread(), "just checking");
// Release the Heap_lock first.
SharedHeap* sh = SharedHeap::heap();
if (sh != NULL) sh->_thread_holds_heap_lock_for_gc = false;
Heap_lock->unlock();
release_and_notify_pending_list_lock();
}
void VM_GC_Operation::release_and_notify_pending_list_lock() {
instanceRefKlass::release_and_notify_pending_list_lock(&_pending_list_basic_lock);
}
对于System.gc的实现,之前写了一篇文章来重点介绍,JVM源码分析之SystemGC完全解读,它会对新生代的老生代都会进行内存回收,这样会比较彻底地回收DirectByteBuffer对象以及他们关联的堆外内存,我们dump内存发现DirectByteBuffer对象本身其实是很小的,但是它后面可能关联了一个非常大的堆外内存,因此我们通常称之为『冰山对象』,我们做ygc的时候会将新生代里的不可达的DirectByteBuffer对象及其堆外内存回收了,但是无法对old里的DirectByteBuffer对象及其堆外内存进行回收,这也是我们通常碰到的最大的问题,如果有大量的DirectByteBuffer对象移到了old,但是又一直没有做cms gc或者full gc,而只进行ygc,那么我们的物理内存可能被慢慢耗光,但是我们还不知道发生了什么,因为heap明明剩余的内存还很多(前提是我们禁用了System.gc)。
为什么要使用堆外内存
DirectByteBuffer在创建的时候会通过Unsafe的native方法来直接使用malloc分配一块内存,这块内存是heap之外的,那么自然也不会对gc造成什么影响(System.gc除外),因为gc耗时的操作主要是操作heap之内的对象,对这块内存的操作也是直接通过Unsafe的native方法来操作的,相当于DirectByteBuffer仅仅是一个壳,还有我们通信过程中如果数据是在Heap里的,最终也还是会copy一份到堆外,然后再进行发送,所以为什么不直接使用堆外内存呢。对于需要频繁操作的内存,并且仅仅是临时存在一会的,都建议使用堆外内存,并且做成缓冲池,不断循环利用这块内存。
为什么不能大面积使用堆外内存
如果我们大面积使用堆外内存并且没有限制,那迟早会导致内存溢出,毕竟程序是跑在一台资源受限的机器上,因为这块内存的回收不是你直接能控制的,当然你可以通过别的一些途径,比如反射,直接使用Unsafe接口等,但是这些务必给你带来了一些烦恼,Java与生俱来的优势被你完全抛弃了—开发不需要关注内存的回收,由gc算法自动去实现。另外上面的gc机制与堆外内存的关系也说了,如果一直触发不了cms gc或者full gc,那么后果可能很严重。
以上就是JVM堆外内存源码完全解读分析的详细内容,更多关于JVM堆外内存源码分析的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!
版权声明:本文内容由网络用户投稿,版权归原作者所有,本站不拥有其著作权,亦不承担相应法律责任。如果您发现本站中有涉嫌抄袭或描述失实的内容,请联系我们jiasou666@gmail.com 处理,核实后本网站将在24小时内删除侵权内容。
发表评论
暂时没有评论,来抢沙发吧~