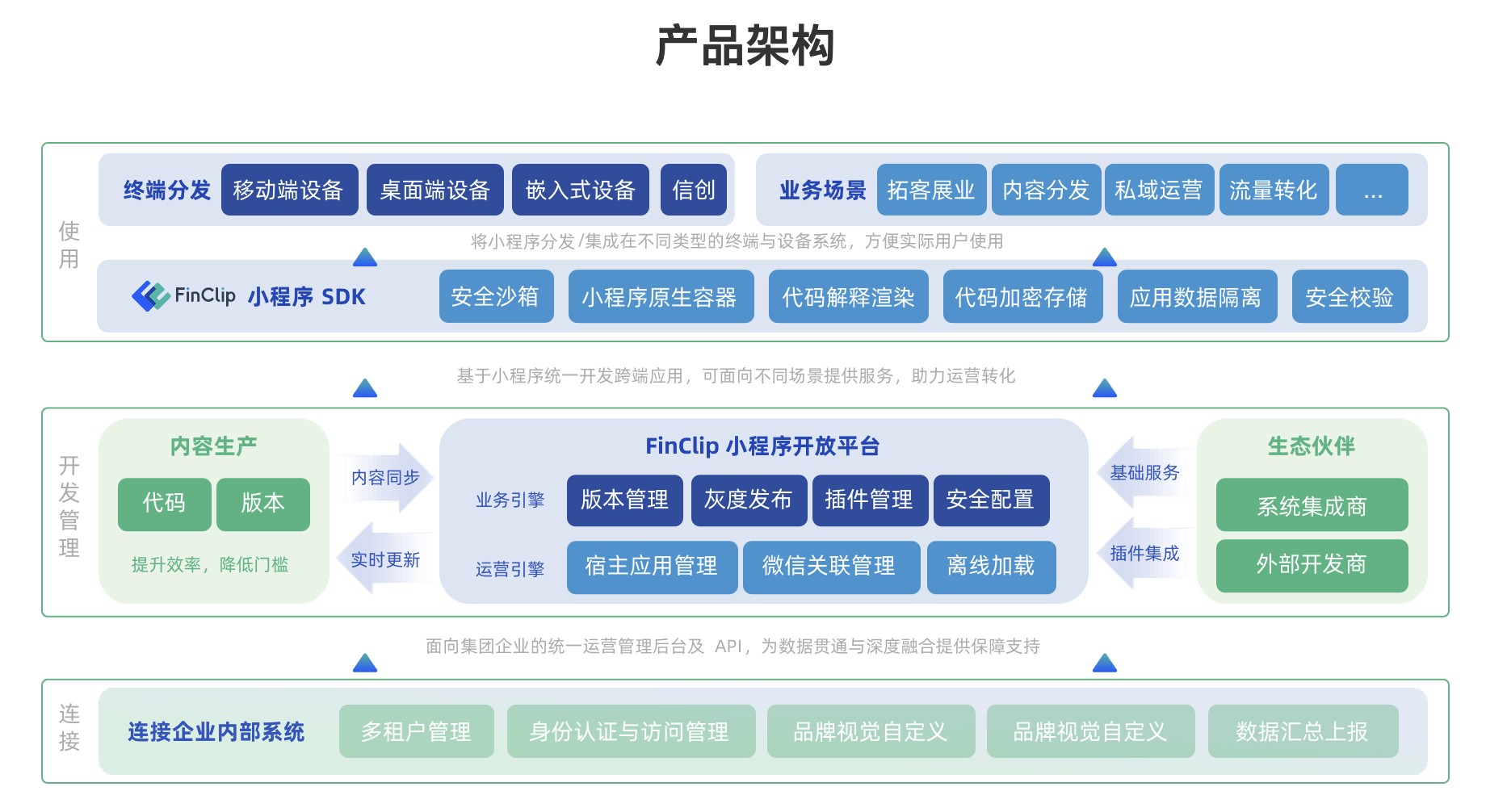
app开发者平台在数字化时代的重要性与发展趋势解析
1131
2022-09-19

.NET Attribute在数据校验上的应用(- framework 3.5是干嘛的)
Attribute(特性)的概念不在此赘述了,相信有点.NET基础的开发人员都明白,用过Attribute的人也不在少数,毕竟很多框架都提供自定义的属性,类似于Newtonsoft.JSON中JsonProperty、JsonIgnore等
自定义特性
.NET 框架允许创建自定义特性,用于存储声明性的信息,且可在运行时被检索。该信息根据设计标准和应用程序需要,可与任何目标元素相关。
创建并使用自定义特性包含四个步骤:
声明自定义特性
构建自定义特性
在目标程序元素上应用自定义特性
通过反射访问特性
声明自定义特性
一个新的自定义特性必须派生自System.Attribute类,例如:
public class FieldDescriptionAttribute : Attribute
{
public string Description { get; private set; }
public FieldDescriptionAttribute(string description)
{
Description = description;
}
}
public class UserEntity
{
[FieldDescription("用户名称")]
public string Name { get; set; }
}
该如何拿到我们标注的信息呢?这时候需要使用反射获取
var type = typeof(UserEntity);
var properties = type.GetProperties();
foreach (var item in properties)
{
if(item.IsDefined(typeof(FieldDescriptionAttribute), true))
{
var attribute = item.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(FieldDescriptionAttribute)) as FieldDescriptionAttribute;
Console.WriteLine(attribute.Description);
}
}
从执行结果上看,我们拿到了我们想要的数据,那么这个特性在实际使用过程中,到底有什么用途呢?
Attribute特性妙用
在实际开发过程中,我们的系统总会提供各种各样的对外接口,其中参数的校验是必不可少的一个环节。然而没有特性时,校验的代码是这样的:
public class UserEntity
{
///
/// 姓名
///
[FieldDescription("用户名称")]
public string Name { get; set; }
///
/// 年龄
///
public int Age { get; set; }
///
/// 地址
///
public string Address { get; set; }
}
UserEntity user = new UserEntity();
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(user.Name))
{
throw new Exception("姓名不能为空");
}
if (user.Age <= 0)
{
throw new Exception("年龄不合法");
}
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(user.Address))
{
throw new Exception("地址不能为空");
}
字段多了之后这种代码就看着非常繁琐,并且看上去不直观。对于这种繁琐又恶心的代码,有什么方法可以优化呢?
使用特性后的验证写法如下:
首先定义一个基础的校验属性,提供基础的校验方法
public abstract class AbstractCustomAttribute : Attribute
{
///
/// 校验后的错误信息
///
public string ErrorMessage { get; set; }
///
/// 数据校验
///
///
public abstract void Validate(object value);
}
然后可以定义常用的一些对应的校验Attribute,例如RequiredAttribute、StringLengthAttribute
///
/// 非空校验
///
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property)]
public class RequiredAttribute : AbstractCustomAttribute
{
public override void Validate(object value)
{
if (value == null || string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(value.ToString()))
{
throw new Exception(string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(ErrorMessage) ? "字段不能为空" : ErrorMessage);
}
}
}
///
/// 自定义验证,验证字符长度
///
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property)]
public class StringLengthAttribute : AbstractCustomAttribute
{
private int _maxLength;
private int _minLength;
public StringLengthAttribute(int minLength, int maxLength)
{
this._maxLength = maxLength;
this._minLength = minLength;
}
public override void Validate(object value)
{
if (value != null && value.ToString().Length >= _minLength && value.ToString().Length <= _maxLength)
{
return;
}
throw new Exception(string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(ErrorMessage) ? $"字段长度必须在{_minLength}与{_maxLength}之间" : ErrorMessage);
}
}
添加一个用于校验的ValidateExtensions
public static class ValidateExtensions
{
///
/// 校验
///
///
///
public static void Validate
{
Type type = entity.GetType();
foreach (var item in type.GetProperties())
{
//需要对Property的字段类型做区分处理针对Object List 数组需要做区分处理
if (item.PropertyType.IsPrimitive || item.PropertyType.IsEnum || item.PropertyType.IsValueType || item.PropertyType == typeof(string))
{
//如果是基元类型、枚举类型、值类型或者字符串 直接进行校验
CheckProperty(entity, item);
}
else
{
//如果是引用类型
var value = item.GetValue(entity, null);
CheckProperty(entity, item);
if (value != null)
{
if ((item.PropertyType.IsGenericType && Array.Exists(item.PropertyType.GetInterfaces(), t => t.GetGenericTypeDefinition() == typeof(IList<>))) || item.PropertyType.IsArray)
{
//判断IEnumerable
var enumeratorMI = item.PropertyType.GetMethod("GetEnumerator");
var enumerator = enumeratorMI.Invoke(value, null);
var moveNextMI = enumerator.GetType().GetMethod("MoveNext");
var currentMI = enumerator.GetType().GetProperty("Current");
int index = 0;
while (Convert.ToBoolean(moveNextMI.Invoke(enumerator, null)))
{
var currentElement = currentMI.GetValue(enumerator, null);
if (currentElement != null)
{
currentElement.Validate();
}
index++;
}
}
else
{
value.Validate();
}
}
}
}
}
private static void CheckProperty(object entity, PropertyInfo property)
{
if (property.IsDefined(typeof(AbstractCustomAttribute), true))//此处是重点
{
//此处是重点
foreach (AbstractCustomAttribute attribute in property.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(AbstractCustomAttribute), true))
{
if (attribute == null)
{
throw new Exception("AbstractCustomAttribute not instantiate");
}
attribute.Validate(property.GetValue(entity, null));
}
}
}
}
新的实体类
public class UserEntity
{
///
/// 姓名
///
[Required]
public string Name { get; set; }
///
/// 年龄
///
public int Age { get; set; }
///
/// 地址
///
[Required]
public string Address { get; set; }
[StringLength(11, 11)]
public string PhoneNum { get; set; }
}
调用方式
UserEntity user = new UserEntity();
user.Validate();
上面的校验逻辑写的比较复杂,主要是考虑到对象中包含复杂对象的情况,如果都是简单对象,可以不用考虑,只需针对单个属性做字段校验
现有的方式是在校验不通过的时候抛出异常,此处大家也可以自定义异常来表示校验的问题,也可以返回自定义的校验结果实体来记录当前是哪个字段出的问题,留待大家自己实现
如果您有更好的建议和想法欢迎提出,共同进步
以上代码均为原创分享,若大家认为有不妥的地方,烦请留言指出,在下感激不尽
出处:https://cnblogs.com/hexu0512/p/12879671.html
版权声明:本文内容由网络用户投稿,版权归原作者所有,本站不拥有其著作权,亦不承担相应法律责任。如果您发现本站中有涉嫌抄袭或描述失实的内容,请联系我们jiasou666@gmail.com 处理,核实后本网站将在24小时内删除侵权内容。
发表评论
暂时没有评论,来抢沙发吧~